Biomass Boiler Uses and Advantages
Biomass boiler technology is a versatile solution that can be used for various purposes such as space heating, hot water production, steam production, or a combination of all three.
One of the main advantages of biomass systems is that they are relatively easy to install. In most cases, they can be retrofitted to replace a fossil fuel boiler without requiring any changes to the downstream heating system, such as radiators or emitters.
Why Switching to Biomass Offers Significant Advantages
- Fuel savings - Heating with biomass can be a lot cheaper. Where there is an existing wood supply, you can see savings of around 80% against oil after factoring in costs for processing the wood
- It is considered carbon neutral as it releases the same amount of CO₂ when burned as the trees have absorbed during their lifetime. The Biomass Energy Centre states it can cut emissions by up to 96% especially if the biomass is obtained from sustainable and local sources.
- Biomass boilers are incredibly efficient heating systems and, when correctly installed and maintained, can have an efficiency of around 80-90%
- Using biomass can qualify you for government Incentives.
How does a biomass boiler work?
How is fuel delivered?
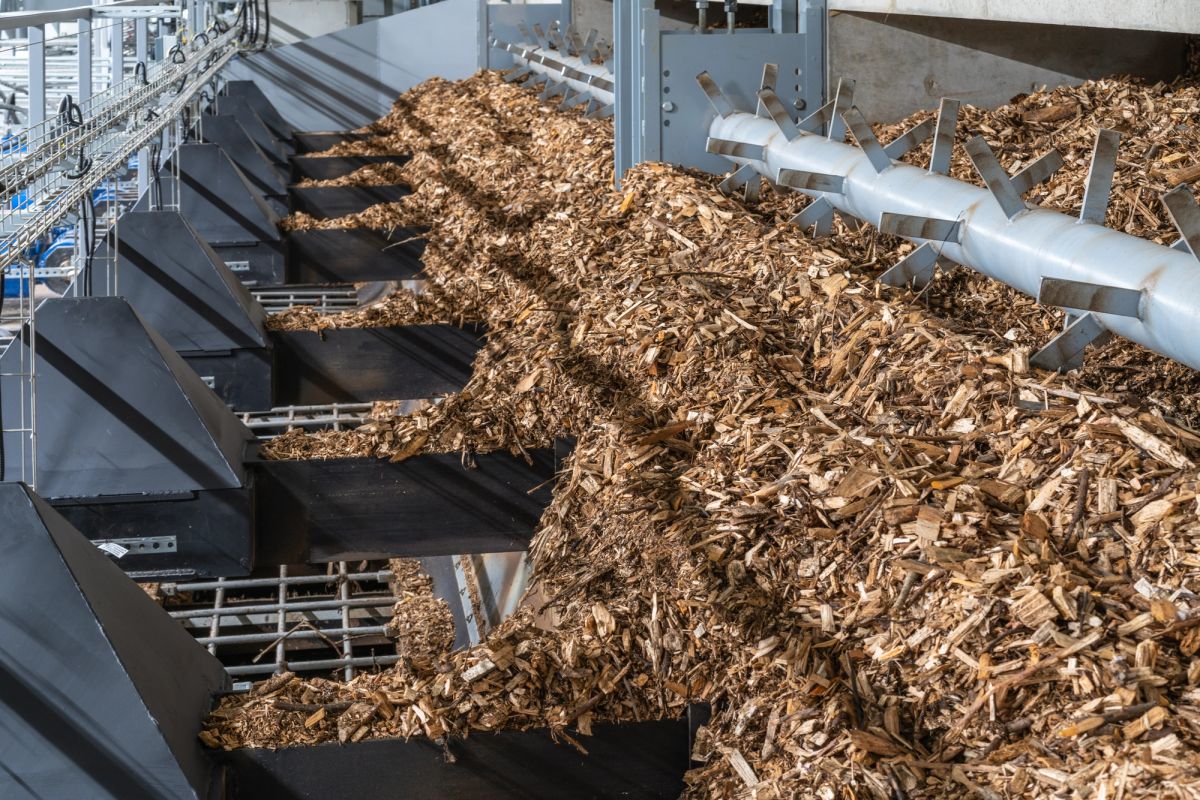
Typically, for a heat boiler, three main types of fuel are used: wood pellets, wood chips, and logs, and sometimes non-woody biomass like miscanthus and cereals. For large commercial systems, fuel is delivered by tanker which blows fuel into a large storage facility; the fuel is then transferred to the boiler via an auger or a suction system.
Why Fuel Analysis is so Important?
When considering biomass boilers, it is crucial to give equal importance to both the operational efficiency of the equipment and the availability of a reliable fuel supply. One common mistake is assuming that the fuel supply will remain consistent over time.
It is essential to evaluate if high-quality fuel can be sourced on multi-year contract terms that align with the boiler's specifications.
Additionally, different settings require specific moisture levels in the fuel. If the air is too dry, burn temperatures may become excessively high, whereas excessive moisture can lead to higher carbon emissions.
Therefore, conducting ongoing research on the fuel supply is essential for optimizing efficiency and minimizing the operational costs associated with biomass boilers.
How do biomass boilers produce heat?
Biomass boilers use a process called gasification to produce heat. There is a two-stage burn process where the fuel is initially burned at temperatures of around 600 °C, which releases gases. These gases are then re-burned, which allows the temperature in the burn chamber to reach around 1,200 °C. The hot gases pass through a metal heat exchanger and then heat the water on the other side.
Thermal stores
Thermal stores are commonly utilised in the majority of installations. These large water tanks serve as heat batteries, efficiently storing the hot water generated by the boiler. The stored hot water is then circulated throughout the central heating system. By incorporating temperature sensors within the thermal store, the biomass boiler can precisely maintain desired temperature levels. When the thermal store's temperature falls below a predefined threshold, the boiler automatically activates to provide heat. On the other hand, if the thermal store reaches a specified temperature, the boiler intelligently shuts off to conserve fuel. This automatic switching mechanism ensures optimal energy utilization and fuel efficiency within the system.
Downstream Heating
The thermal store has a main system pump to circulate the warm water to the building(s). Each end user point sends a signal back to the biomass plant room when there is a demand for heat, which results in the pump circulating the hot water. Pipework connects the buildings to the plant room, which can be above or below ground, depending on the site. Multiple buildings can connect to the same biomass boiler; this is called district heating.
Harnessing biomass energy: CoolPlanet can help
In the ever-evolving landscape of global energy, biomass energy has emerged as a pivotal player. Its potential to drastically curtail carbon emissions, particularly in challenging-to-decarbonise sectors like aviation, transport, and manufacturing, cannot be overstated.
However, the significance of involving a professional, equipped with proven and pertinent expertise, at the project's design inception also cannot be emphasised enough. With CoolPlanet by your side, the journey to a meticulously designed and cost-efficient biomass system becomes a reality.